For surgically treated fractures with residual steps and diastases after operation the correlation between steps and 2 year outcome was good.
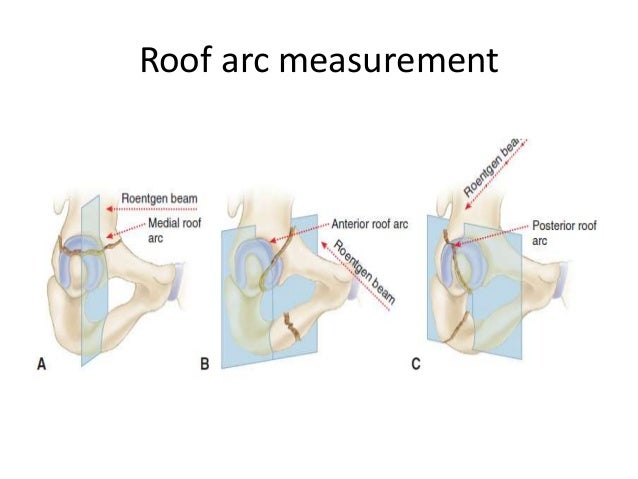
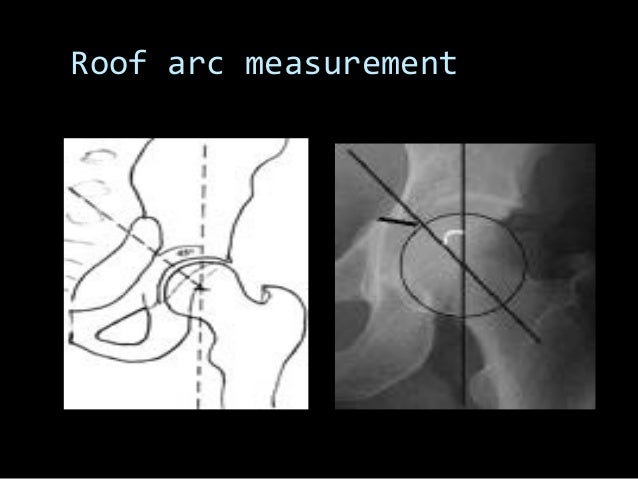
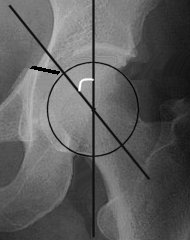
Roof arc angle acetabular fracture.
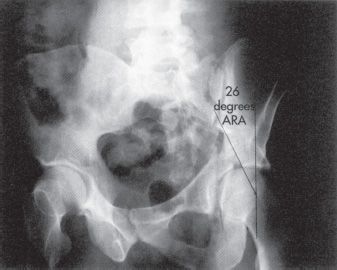
The medial roof arc angle was 46 6 3 anterior roof arc angle was 52 7 0 and posterior roof arc angle was 62 8 5.
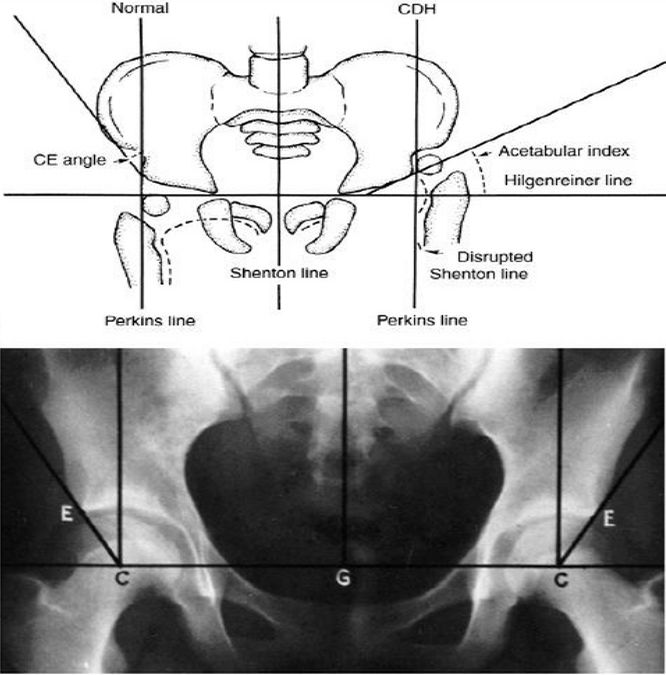
Transverse acetabular fractures involve a single fracture line which crosses the acetabulum through both posterior and anterior columns.
Such fractures divide the acetabulum into an upper portion ilium with the roof and a lower portion ischium and pubis.
Acetabular fracture displacement and roof arc angles converted into a roof arc score were assessed and correlated with clinical outcome at 2 years follow up.
Acetabular fracture involves whether superior articular weight bearing area and stability of the hip are assessed by acetabular roof arc angles comprising medial anterior and posterior.
In acetabular fracture a medial roof arc angle less than 46 degrees an anterior roof arc angle less than 52 degrees or posterior roof arc angle less than 61 degrees is considered to be involved in a weight bearing area.
Many previous studies based on clinical biomechanics and anatomic superior articular surface of acetabulum showed different degrees of the angles.